Attribuut-taxonomieën (WooCommerce): verschil tussen versies
| (32 tussenliggende versies door dezelfde gebruiker niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
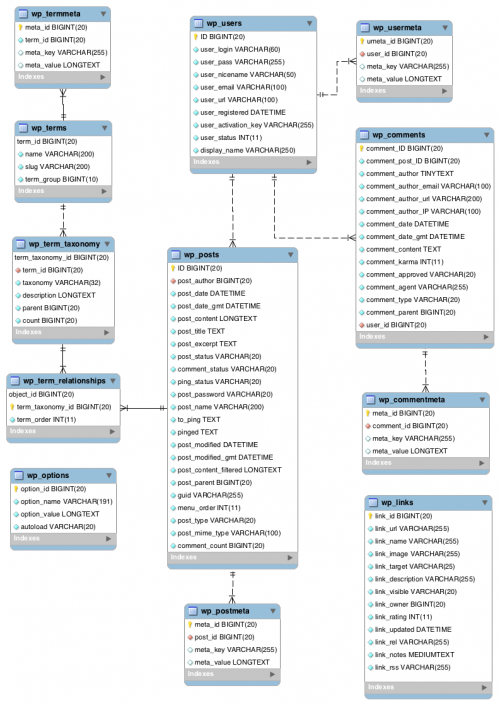
[[file:20190529-1146.png|500px|thumb|Database-model van vermoedelijk WordPress 4.4. Ietwat achterhaald, maar prima om een indruk te krijgen]] | [[file:20190529-1146.png|500px|thumb|Database-model van vermoedelijk WordPress 4.4. Ietwat achterhaald, maar prima om een indruk te krijgen]] | ||
| − | WooCommerce' | + | WooCommerce kent drie taxonomische systemen: ''[[Product cat-Taxonomieën (WordPress) | product_cat-Categorieën]]'' (veelzijdig maar soms zwaar), ''Tags'' (ongrepen & onbemind) en ''Attributes'' (beperkt maar soms zwaar, ''Kenmerken'' of ''Eigenschappen'' in het Nederlands). Dit artikel gaat over dit laatste systeem. |
| − | '' | + | ''Attributes'' komen in twee smaken: |
* ''Predefined Attributes'' | * ''Predefined Attributes'' | ||
* ''Custom Attributes''. | * ''Custom Attributes''. | ||
| − | Dit hoofdstuk gaat voornamelijk over deze eerste variant. | + | Dit hoofdstuk gaat voornamelijk over deze eerste variant en in het bijzonder over het programmeren ervan. |
| + | |||
| + | == Performance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Verhuisd naar [[Attributes vs. categories (WooCommerce)#Evaluatie: Attributes vs. categories | Attributes vs. Categories » Evaluatie]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Voorbeeld == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Waarschijnlijk zegt dit een hoop: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | ############################################################### | ||
| + | # "Automatic Stop" - Define main taxon & subtaxons | ||
| + | ############################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Define main taxon: "Automatische stop" | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $attribute_definition = array | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | 'attribute_name' => 'automatische stop', | ||
| + | 'attribute_label' => 'Automatische stop', | ||
| + | 'attribute_type' => 'select', | ||
| + | 'attribute_orderby' => 'menu_order', | ||
| + | 'attribute_public' => true | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | # dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy() | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Internally, this code is used for the actual taxonomy creation: | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # $wpdb->insert( $wpdb->prefix . 'woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies', $attribute ); | ||
| + | # do_action( 'woocommerce_attribute_added', $wpdb->insert_id, $attribute ); | ||
| + | # flush_rewrite_rules(); | ||
| + | # delete_transient( 'wc_attribute_taxonomies' ); | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute_definition); | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Subtaxon: Met automatische stop | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $term = "Met automatische stop"; | ||
| + | $taxonomy = "pa_automatische-stop"; | ||
| + | $args = array | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | 'description' => 'Alle koolborstels die zijn voorzien van een automatische stop' | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Subtaxon: Zonder automatische stop | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $term = "Zonder automatische stop"; | ||
| + | $taxonomy = "pa_automatische-stop"; | ||
| + | $args = array | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | 'description' => 'Alle koolborstels die niet zijn voorzien van een automatische stop' | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ############################################################### | ||
| + | # "Cable" - Defineer hoofdtaxon & subtaxons | ||
| + | ############################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Defineer hoofdtaxon | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $attribute_definition = array | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | 'attribute_name' => 'stroomdraad', | ||
| + | 'attribute_label' => 'Stroomdraad', | ||
| + | 'attribute_type' => 'select', | ||
| + | 'attribute_orderby' => 'menu_order', | ||
| + | 'attribute_public' => true | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute_definition); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Defineer subtaxon "With cable" | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $term = "Met stroomdraad"; | ||
| + | $taxonomy = "pa_stroomdraad"; | ||
| + | $args = array('description' => 'Alle koolborstels met aansluit-stroomdraad'); | ||
| + | wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args); | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Defineer subtaxon "Without cable" | ||
| + | ##################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $term = "Zonder stroomdraad"; | ||
| + | $taxonomy = "pa_stroomdraad"; | ||
| + | $args = array('description' => 'Alle koolborstels zonder aansluit-stroomdraad'); | ||
| + | wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | En de bijbehorende functie <code>dvb_add_attribute_taxonony</code> (inclusief uitleg waarom ik hier in hemelsnaam een eigen functie voor gebruik): | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | ####################################################################################### | ||
| + | ####################################################################################### | ||
| + | # dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy | ||
| + | ####################################################################################### | ||
| + | ####################################################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # * Somehow, the usual function register_taxonomy doesn't work for WooCommerce Attributes, hence the | ||
| + | # lower-level approach in this function | ||
| + | # * Based on the example https://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/244335/creating-custom-woocommerce-attribute-taxonomies-from-a-plugin | ||
| + | # * Jeroen Strompf, De Vliegende Brigade - April 2019 | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | function dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # Get acces to $wpdb class | ||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | global $wpdb; | ||
| + | |||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # Verify input | ||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | if (empty($attribute['attribute_type'])) { $attribute['attribute_type'] = 'text';} | ||
| + | if (empty($attribute['attribute_orderby'])) { $attribute['attribute_orderby'] = 'menu_order';} | ||
| + | if (empty($attribute['attribute_public'])) { $attribute['attribute_public'] = 0;} | ||
| + | if (empty( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) || empty( $attribute['attribute_label'] ) ) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | return new WP_Error( 'error', __( 'Attribute name and/and slug is missing.', 'woocommerce' ) ); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | elseif ( ( $valid_attribute_name = dvb_check_attribute_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) && is_wp_error( $valid_attribute_name ) ) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | return $valid_attribute_name; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | elseif ( taxonomy_exists( wc_attribute_taxonomy_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) ) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | return new WP_Error( 'error', sprintf( __( 'Slug "%s" already in use', 'woocommerce' ), sanitize_title( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) ); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # Insert into WordPress | ||
| + | ################################################################################### | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # The array field names must correspond with the table column names in the tabel | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | $wpdb->insert( $wpdb->prefix . 'woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies', $attribute ); | ||
| + | |||
| + | do_action( 'woocommerce_attribute_added', $wpdb->insert_id, $attribute ); | ||
| + | |||
| + | flush_rewrite_rules(); | ||
| + | delete_transient( 'wc_attribute_taxonomies' ); | ||
| + | |||
| + | return true; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wat je zoal uit dit voorbeeld kunt halen: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Er is eigenlijk maar één attribuut-taxonomie, en wat 'taxonomieën' lijken te zijn, zijn eigenlijk ''hoofdtaxons'' - Zo noem ik ze ook | ||
== Database-tabellen == | == Database-tabellen == | ||
| Regel 14: | Regel 175: | ||
=== wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies === | === wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies === | ||
| − | Tabel <code>wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies</code> | + | Tabel <code>wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies</code> Lijkt niets te doen. Zie hoodstuk over verwijdering van attribuut-taxonomieën, elders in dit artikel: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Regel 298: | Regel 459: | ||
== Verwijderen == | == Verwijderen == | ||
| − | + | Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen? → [[Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen (WooCommerce)| Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen]] | |
| − | + | == Attributes benaderen via UI == | |
| − | + | Een ogenschijnlijk simpele vraag: Hoe kan ik handmatig de attributen van een product wijzigen? Onderaan de productkaart, heb je notabene een apart gedeelte voor het beheren van attributes. Maar toch lijkt dat niet zomaar te lukken: De velden zijn leeg. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/issues/19552]: Verander op de productkaart het type product in ''Variable product''. Nu zou het werken → Werkt nog steeds niet. Ook niet als ik 't product eerst opsla als type ''Variable product'' en daarna het scherm ververs. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Wat wél werkt: Ik kan attributen bijwerken door gewoon de nieuwe waardes in te voeren. Oude waardes verdwijnen daarbij. | |
| − | ' | + | == Old attributes don't show up == |
| − | + | In May 2023, we had the following problem/case: | |
| − | + | * We wanted to add an attribute to an existing product | |
| − | + | * This product had already a bunch of attributes associated with it, but they weren't shown at the product edit page » Product data » Attributes | |
| − | + | * What would happen if this product would get associated with a new attribute? Would the old associations be overwritten? | |
| − | + | * Copying this product to a new product (for testing) didn't help: All attributes got lost while copying (product categorie associates were included in copying, though). | |
== Zie ook == | == Zie ook == | ||
| + | * [[Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen (WooCommerce)]] | ||
| + | * [[Categorieën (WordPress)]] | ||
* [[PHP-API (WordPress)#wp_insert_term | PHP-API » wp_insert_term]] | * [[PHP-API (WordPress)#wp_insert_term | PHP-API » wp_insert_term]] | ||
| + | * [[Taxonomieën (WordPress)]] | ||
== Bronnen == | == Bronnen == | ||
| Regel 381: | Regel 490: | ||
* https://codex.wordpress.org/images/2/25/WP4.4.2-ERD.png | * https://codex.wordpress.org/images/2/25/WP4.4.2-ERD.png | ||
* https://codex.wordpress.org/WordPress_Taxonomy#wp_term_taxonomy | * https://codex.wordpress.org/WordPress_Taxonomy#wp_term_taxonomy | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Attributes niet zichtbaar op productkaart === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * https://www.google.com/search?q=woocommerce+attributes+not+visible+on+product+page&oq=woocommerce&aqs=chrome.0.69i59j69i57j69i59l2j0l2j69i60l4.2177j1j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 | ||
| + | * https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/issues/19552 | ||
| + | * https://docs.woocommerce.com/document/variable-product/ | ||
| + | * https://wordpress.org/support/topic/product-attributes-without-variation-dont-display/ | ||
| + | * https://wordpress.org/support/topic/woocommerce-product-attributes-and-categories-not-displayed/ - Vermoedelijk hetzelfde probleem als wat ik heb | ||
Huidige versie van 11 mei 2023 om 11:56
WooCommerce kent drie taxonomische systemen: product_cat-Categorieën (veelzijdig maar soms zwaar), Tags (ongrepen & onbemind) en Attributes (beperkt maar soms zwaar, Kenmerken of Eigenschappen in het Nederlands). Dit artikel gaat over dit laatste systeem.
Attributes komen in twee smaken:
- Predefined Attributes
- Custom Attributes.
Dit hoofdstuk gaat voornamelijk over deze eerste variant en in het bijzonder over het programmeren ervan.
Performance
Verhuisd naar Attributes vs. Categories » Evaluatie
Voorbeeld
Waarschijnlijk zegt dit een hoop:
###############################################################
# "Automatic Stop" - Define main taxon & subtaxons
###############################################################
#
# Define main taxon: "Automatische stop"
#####################################
#
$attribute_definition = array
(
'attribute_name' => 'automatische stop',
'attribute_label' => 'Automatische stop',
'attribute_type' => 'select',
'attribute_orderby' => 'menu_order',
'attribute_public' => true
);
# dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy()
#####################################
#
# Internally, this code is used for the actual taxonomy creation:
#
# $wpdb->insert( $wpdb->prefix . 'woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies', $attribute );
# do_action( 'woocommerce_attribute_added', $wpdb->insert_id, $attribute );
# flush_rewrite_rules();
# delete_transient( 'wc_attribute_taxonomies' );
#
dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute_definition);
# Subtaxon: Met automatische stop
#####################################
#
$term = "Met automatische stop";
$taxonomy = "pa_automatische-stop";
$args = array
(
'description' => 'Alle koolborstels die zijn voorzien van een automatische stop'
);
wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args);
# Subtaxon: Zonder automatische stop
#####################################
#
$term = "Zonder automatische stop";
$taxonomy = "pa_automatische-stop";
$args = array
(
'description' => 'Alle koolborstels die niet zijn voorzien van een automatische stop'
);
wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args);
###############################################################
# "Cable" - Defineer hoofdtaxon & subtaxons
###############################################################
#
# Defineer hoofdtaxon
#####################################
#
$attribute_definition = array
(
'attribute_name' => 'stroomdraad',
'attribute_label' => 'Stroomdraad',
'attribute_type' => 'select',
'attribute_orderby' => 'menu_order',
'attribute_public' => true
);
dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute_definition);
# Defineer subtaxon "With cable"
#####################################
#
$term = "Met stroomdraad";
$taxonomy = "pa_stroomdraad";
$args = array('description' => 'Alle koolborstels met aansluit-stroomdraad');
wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args);
# Defineer subtaxon "Without cable"
#####################################
#
$term = "Zonder stroomdraad";
$taxonomy = "pa_stroomdraad";
$args = array('description' => 'Alle koolborstels zonder aansluit-stroomdraad');
wp_insert_term($term, $taxonomy, $args);
En de bijbehorende functie dvb_add_attribute_taxonony (inclusief uitleg waarom ik hier in hemelsnaam een eigen functie voor gebruik):
#######################################################################################
#######################################################################################
# dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy
#######################################################################################
#######################################################################################
#
# * Somehow, the usual function register_taxonomy doesn't work for WooCommerce Attributes, hence the
# lower-level approach in this function
# * Based on the example https://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/244335/creating-custom-woocommerce-attribute-taxonomies-from-a-plugin
# * Jeroen Strompf, De Vliegende Brigade - April 2019
#
function dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute)
{
###################################################################################
# Get acces to $wpdb class
###################################################################################
#
global $wpdb;
###################################################################################
# Verify input
###################################################################################
#
if (empty($attribute['attribute_type'])) { $attribute['attribute_type'] = 'text';}
if (empty($attribute['attribute_orderby'])) { $attribute['attribute_orderby'] = 'menu_order';}
if (empty($attribute['attribute_public'])) { $attribute['attribute_public'] = 0;}
if (empty( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) || empty( $attribute['attribute_label'] ) )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', __( 'Attribute name and/and slug is missing.', 'woocommerce' ) );
}
elseif ( ( $valid_attribute_name = dvb_check_attribute_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) && is_wp_error( $valid_attribute_name ) )
{
return $valid_attribute_name;
}
elseif ( taxonomy_exists( wc_attribute_taxonomy_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', sprintf( __( 'Slug "%s" already in use', 'woocommerce' ), sanitize_title( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) );
}
###################################################################################
# Insert into WordPress
###################################################################################
#
# The array field names must correspond with the table column names in the tabel
#
$wpdb->insert( $wpdb->prefix . 'woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies', $attribute );
do_action( 'woocommerce_attribute_added', $wpdb->insert_id, $attribute );
flush_rewrite_rules();
delete_transient( 'wc_attribute_taxonomies' );
return true;
};
Wat je zoal uit dit voorbeeld kunt halen:
- Er is eigenlijk maar één attribuut-taxonomie, en wat 'taxonomieën' lijken te zijn, zijn eigenlijk hoofdtaxons - Zo noem ik ze ook
Database-tabellen
wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies
Tabel wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies Lijkt niets te doen. Zie hoodstuk over verwijdering van attribuut-taxonomieën, elders in dit artikel:
SELECT * FROM kbo3.wp_woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies; attribute_id attribute_name attribute_label attribute_type attribute_orderby attribute_public ------------ -------------- ----------------- -------------- ----------------- ---------------- 5 breedte Breedte text name_num 1 6 diepte Diepte text name_num 1 7 lengte Lengte text name_num 1 8 automatische_stop Automatische stop text name 1
wp_terms
Subtaxons verschijnen gewoon in wp_terms. Dat maakt het gemakkelijk om met subtaxons te werken, want het werkt hetzelfde als voor gewone categorieën.
wp_term_taxonomy
Tabel wp_term_taxonomy verbindt taxons met taxonomieën. Hier kun je zien dat WooCommerce 'onder water' losse taxonomieën defineert voor alle attributen. Je herkent ze aan de prefix pa_. Merk op dat parent=0: Er wordt niet gebruik gemaakt van hierarchie! Ook niet zo vreemd, omdat je bij attributen max. twee lagen hebt. Voorbeeld:
SELECT * FROM kbo3.wp_term_taxonomy where taxonomy like "pa_%"; term_taxonomy_id term_id taxonomy description parent count ---------------- ------- ---------- ------------- ------ ----- 110 110 pa_breedte Breedte-taxon 0 0
wp_term_relationships
Tabel wp_term_relationships verbindt taxons met WordPress-objecten.
wp_termmeta
Tabel wp_termmeta lijkt metadata te bevatten: Als je nog iets extra's kwijt wilt over een taxon, kun je dat hier doen. WooCommerce maakt hier bv. voor product_cat-taxonomieën aan, om de count per hoofdtaxon in op te slaan.
Het lijkt vooralsnog niet gebruikt te worden voor attribuut-taxonomieën.
Database-velden
In het algemeen zijn veldnamen binnen een WordPress-instantie niet consistent. Dat kun je zien aan het ER-diagram elders in dit artikel:
- In tabel wp_users heet de pk ID
- In tabel wp_usermeta heet dit veld user_id
- In tabel wp_posts heet dit veld post_author.
Desalniettemin: Rondom taxonomieën lijken veldnamen consistent te zijn. Anders had dit hoofdstuk weinig zin.
term_id
term_id is de pk voor een taxon of term.
term_taxonomy_id
term_taxonomy_idis de pk van de tussentabelwp_term_taxonomy, die ervoor zorgt dat je een many-to-many-relatie hebt tussentermsenterm_relationships- Zo'n veel-veel-relatie ben ik tot op heden nog niet tegengekomen. Vandaar dat deze twee velden steeds dezelfde waardes lijken te hebben: Er zijn dan evenveel records in beide tabellen
- Overigens: Ik heb geen idee waarom je zo'n veel-veel-relatie wilt hebben, maar daar gaat het nu niet om.
UI-Velden
Dit zijn de velden die ik zoal in de user interface tegenkom. Namen zijn inconsistent en niet-intuïtief
Name - attribute_name
Shown on the front-end
Slug - attribute_label
Max. 28 karakters.
attribute_type
Het soort control dat gebruikt wordt als interface??? Bv.:
select- Beperkt aantal keuzes, zoals een lookup-tabel of voor Boolese waardentext- Tekstveld, lijkt me.
Enable Archives
Dus dat je een 'taxon-pagina' hebt. Altijd doen. Voor Attributes-taxonomieën kun je helaas geen afbeelding of tekst toevoegen (itt. gewone Categorieën) [1]
Custom ordering - attribute_orderby
Niet zo spannend:
menu_ordername- etc.
attribute_public
Taxonomieën worden binnen een WordPress-site veelvuldig gebruikt voor interne aangelegenheden. Bv. om vertalingen bij te houden. Vandaar dat je er voor kunt kiezen om attribuut-taxonomieën verborgen te houden voor gebruikers.
Taxonomie toevoegen
Met taxonomie bedoel ik hier hetzelfde als hoofdtaxon .
Toevoegen van een hoofdtaxon/taxonomie, wil niet lukken met bv. wp_insert_term. Aangezien Attributes een speciaal geval is van een categorie, zou je verwachten dat dit werkt. Maar dat doet het niet. Gelukkig kun je dit op een meer low-level fixen mbv. $wpdb. Daar gebruik ik deze functies voor. Deze staat in één van m'n libraries (niet in functions.php). Geïnspireerd op [2]:
function dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute)
{
# Add a WooCommerce Attribute-taxonomy
#######################################################################################################
#
# * Somehow, the usual function register_taxonomy doesn't work for WooCommerce Attributes, hence the
# lower-level approach in this function
# * Based on the example https://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/244335/creating-custom-woocommerce-attribute-taxonomies-from-a-plugin
# * Jeroen Strompf, De Vliegende Brigade - April 2019
# * To be included in functions.php where appropriate
#######################################################################################################
# Get acces to $wpdb class
#######################################################################################################
#
global $wpdb;
#######################################################################################################
# Verify input
#######################################################################################################
#
if (empty($attribute['attribute_type'])) { $attribute['attribute_type'] = 'text';}
if (empty($attribute['attribute_orderby'])) { $attribute['attribute_orderby'] = 'menu_order';}
if (empty($attribute['attribute_public'])) { $attribute['attribute_public'] = 0;}
if (empty( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) || empty( $attribute['attribute_label'] ) )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', __( 'Attribute name and/and slug is missing.', 'woocommerce' ) );
}
elseif ( ( $valid_attribute_name = dvb_check_attribute_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) && is_wp_error( $valid_attribute_name ) )
{
return $valid_attribute_name;
}
elseif ( taxonomy_exists( wc_attribute_taxonomy_name( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', sprintf( __( 'Slug "%s" already in use', 'woocommerce' ), sanitize_title( $attribute['attribute_name'] ) ) );
}
#######################################################################################################
# Insert into WordPress
#######################################################################################################
#
$wpdb->insert( $wpdb->prefix . 'woocommerce_attribute_taxonomies', $attribute );
do_action( 'woocommerce_attribute_added', $wpdb->insert_id, $attribute );
flush_rewrite_rules();
delete_transient( 'wc_attribute_taxonomies' );
return true;
};
function dvb_check_attribute_name( $attribute_name )
{
# Check if a given attribute name is valid
#######################################################################################################
#
# * Based on the example https://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/244335/creating-custom-woocommerce-attribute-taxonomies-from-a-plugin
# * Jeroen Strompf, De Vliegende Brigade - April 2019
# * To be included in functions.php where appropriate
if ( strlen( $attribute_name ) >= 28 )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', sprintf( __( 'Slug "%s" is longer than 28 characters)', 'woocommerce' ), sanitize_title( $attribute_name ) ) );
}
elseif ( wc_check_if_attribute_name_is_reserved( $attribute_name ) )
{
return new WP_Error( 'error', sprintf( __( 'Slug "%s" is not allowed because it is a reserved term.', 'woocommerce' ), sanitize_title( $attribute_name ) ) );
}
return true;
};
Voorbeeld van een aanroep:
<?php
###############################################################
# Call require_once
###############################################################
#
# Functions "dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy" and
# "dvb_check_attribute_name" have been included in functions.php.
# They become available through this "require_once" command
#
require_once("/home/strompf/www/example.com/wp-load.php");
###############################################################
# Define new attribute-taxonomy
###############################################################
#
$attribute_definition = array
(
'attribute_name' => 'attribute-naam (2)',
'attribute_label' => 'attribute-plakker (2)',
'attribute_type' => 'text',
'attribute_orderby' => 'menu_order',
'attribute_public' => false
);
###############################################################
# Create this new attribute-taxonomy
###############################################################
#
dvb_add_attribute_taxonomy($attribute_definition);
Subtaxons toevoegen
- Attribuut-taxonomieën zijn niet-hiërarchisch, en zitten iets anders in elkaar dan product_cat-taxonomieën:
- Subtaxons toevoegen, gaat op dezelfde manier als voor product_cat-taxonomieën, met één verschil: De naam van de taxonomie, is de naam, voorafgegaan door
pa_ - De gebruikelijke API-functie hiervoor:
wp_insert_term
Voorbeeld uit een SQL-script, waarbij pa_breedte de betreffende taxonomie is:
# Create table
##############
#
create table dim1_taxons_tmp
select distinct
dim1,
concat
(
"wp_insert_term('",
replace(dim1, ".", ","),"'",
", 'pa_breedte',",
" array('description' => 'Alle koolborstels met een breedte van ",replace(dim1, ".", ",")," mm',",
" 'parent' => 0, 'slug' => 'breedte-",replace(dim1, "," ,""),"' ));"
) as dim1_php
from root_tmp;
Je weet de 'pa-naam' pas met zekerheid, nadat er subtaxons zijn aangemaakt. Dan vind je 'm terug met zoiets als dit (in SQL):
SELECT distinct taxonomy FROM example_com.wp_term_taxonomy;
Mochten er nog geen taxons zijn toegevoegd:
- Voeg er eentje handmatig toe, om het te testen
- Gebruik je gezond verstand om uit te vogelen wat de naam zou zijn.
Nog één voorbeeld:
<?php
require_once("/var/www/kbo3.dvb/wp-load.php");
wp_insert_term
(
'Met automatische stop' ,
'pa_automatische_stop',
array
(
'description' => 'Alle koolborstels met automatische stop',
'parent' => 0,
'slug' => 'met-automatische-stop'
)
);
wp_insert_term
(
'Zonder automatische stop' ,
'pa_automatische_stop',
array
(
'description' => 'Alle koolborstels zonder automatische stop',
'parent' => 0,
'slug' => 'zonder-automatische-stop'
)
);
Verwijderen
Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen? → Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen
Attributes benaderen via UI
Een ogenschijnlijk simpele vraag: Hoe kan ik handmatig de attributen van een product wijzigen? Onderaan de productkaart, heb je notabene een apart gedeelte voor het beheren van attributes. Maar toch lijkt dat niet zomaar te lukken: De velden zijn leeg.
[3]: Verander op de productkaart het type product in Variable product. Nu zou het werken → Werkt nog steeds niet. Ook niet als ik 't product eerst opsla als type Variable product en daarna het scherm ververs.
Wat wél werkt: Ik kan attributen bijwerken door gewoon de nieuwe waardes in te voeren. Oude waardes verdwijnen daarbij.
Old attributes don't show up
In May 2023, we had the following problem/case:
- We wanted to add an attribute to an existing product
- This product had already a bunch of attributes associated with it, but they weren't shown at the product edit page » Product data » Attributes
- What would happen if this product would get associated with a new attribute? Would the old associations be overwritten?
- Copying this product to a new product (for testing) didn't help: All attributes got lost while copying (product categorie associates were included in copying, though).
Zie ook
- Attribuut-taxonomieën verwijderen (WooCommerce)
- Categorieën (WordPress)
- PHP-API » wp_insert_term
- Taxonomieën (WordPress)
Bronnen
- https://wordpress.org/support/topic/term_taxonomy_id-vs-term_id/
- https://codex.wordpress.org/images/2/25/WP4.4.2-ERD.png
- https://codex.wordpress.org/WordPress_Taxonomy#wp_term_taxonomy
Attributes niet zichtbaar op productkaart
- https://www.google.com/search?q=woocommerce+attributes+not+visible+on+product+page&oq=woocommerce&aqs=chrome.0.69i59j69i57j69i59l2j0l2j69i60l4.2177j1j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
- https://github.com/woocommerce/woocommerce/issues/19552
- https://docs.woocommerce.com/document/variable-product/
- https://wordpress.org/support/topic/product-attributes-without-variation-dont-display/
- https://wordpress.org/support/topic/woocommerce-product-attributes-and-categories-not-displayed/ - Vermoedelijk hetzelfde probleem als wat ik heb